Machine Learning Prediction of Age and Alzheimer's Disease from DNA Methylation Profiles
/
DATA SCIENCE / MACHINE LEARNING
Developed an end‑to‑end machine learning pipeline to predict biological age and Alzheimer’s disease risk from large‑scale DNA methylation profiles, transforming raw high‑dimensional genomic data into actionable clinical insights through rigorous data preprocessing, feature engineering, and model optimization. Applied statistical analysis and dimensionality reduction techniques to identify predictive epigenetic markers, then trained and evaluated supervised learning models (including regularized algorithms and tree‑based methods) using cross‑validation, performance benchmarking, and error analysis to ensure robustness and generalizability. Focused on model interpretability and reproducibility by documenting the full data workflow, validating results against published findings, and highlighting implications for early detection, chronic disease management, and personalized medicine
Technical Skills and Methods
Machine Learning & Model Development
Gradient Boosting Frameworks: Implemented LightGBM (LGBMRegressor, LGBMClassifier) for regression and classification tasks on high-dimensional datasets with 450K-850K features
Hyperparameter Optimization: Utilized Optuna for automated hyperparameter tuning to maximize model performance
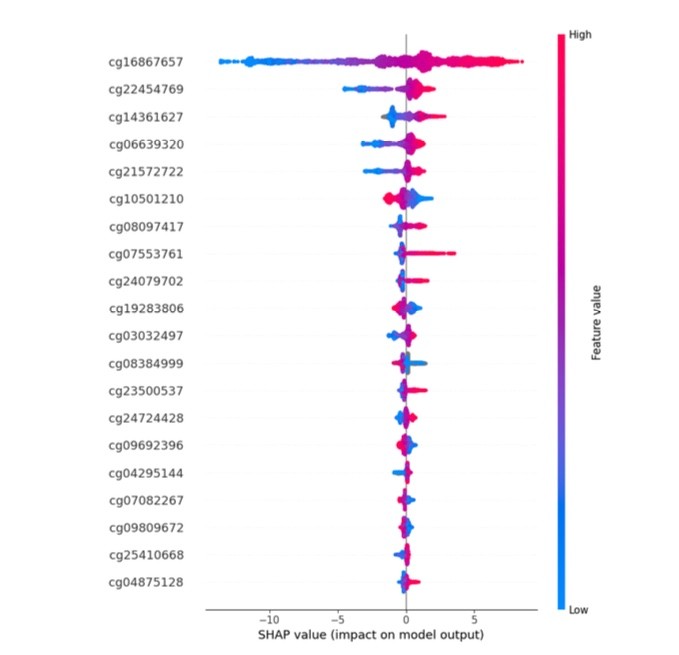
Model Interpretability: Applied SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) values for feature importance analysis and model explanation
Cross-Validation: Performed k-fold cross-validation to ensure robust model generalization and prevent overfitting
Data Processing & Feature Engineering
High-Dimensional Data Management: Engineered efficient chunking strategies to handle datasets with 485K-893K features while managing computational constraints
Missing Data Handling: Developed preprocessing pipelines to address datasets with 368K-510K missing values across multiple features
Feature Selection: Extracted top contributing features (500 CpG sites) from large feature spaces using SHAP-based importance ranking
Data Integration: Merged multi-platform datasets (Illumina 450K and 850K arrays) while managing platform-specific missing data
Statistical Analysis
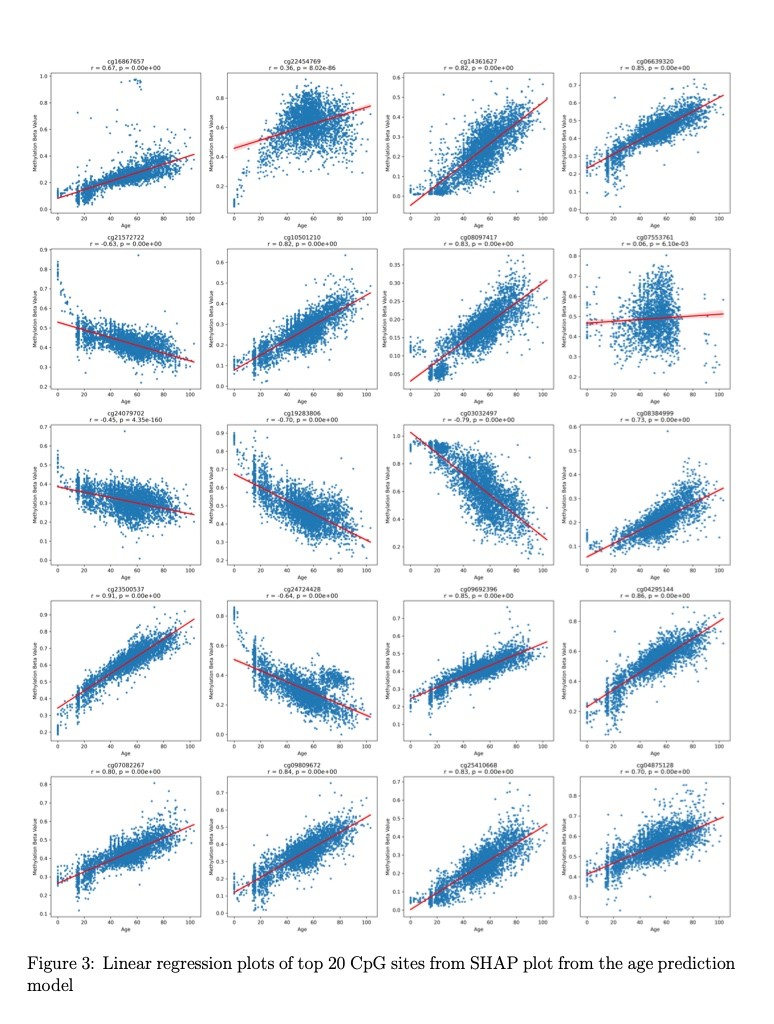
Correlation Analysis: Conducted Pearson correlation coefficient analysis to assess relationships between methylation patterns and target variables
Linear Regression: Performed regression analysis on individual features to validate biological relevance
P-value Interpretation: Applied statistical significance testing for feature validation
Data Visualization
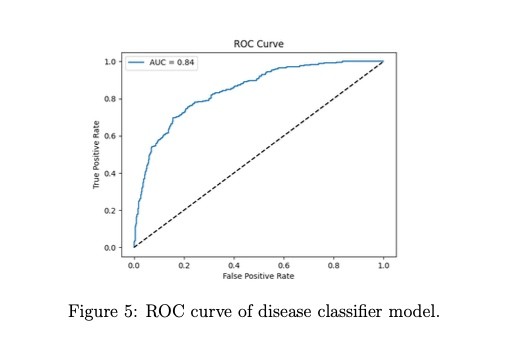
Model Performance Metrics: Created confusion matrices, ROC curves (AUC), and evaluation metric tables
Feature Analysis Plots: Developed SHAP summary plots, scatter plots with regression lines, and distribution visualizations
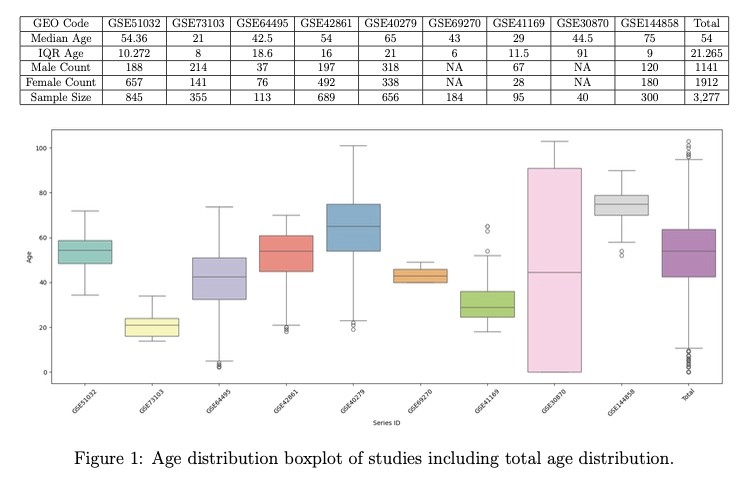
Data Distribution: Generated boxplots and age distribution analyses across multi-study datasets
Bioinformatics & Domain Knowledge
Genomic Data Analysis: Processed DNA methylation β-values from Illumina BeadChip arrays (450K, 850K platforms)
Gene Annotation: Utilized R packages (IlluminaHumanMethylation450kanno, IlluminaHumanMethylationEPICanno) for CpG-to-gene mapping
Public Database Navigation: Retrieved and processed datasets from NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database
Biological Validation: Connected machine learning findings to established biological markers and literature
Programming & Tools
Python: Primary language for data processing, modeling, and analysis
R: Used for genomic annotation and methylation data processing
Version Control: Maintained project repository on GitHub for reproducibility
Model Evaluation
Regression Metrics: Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Median Absolute Error (MedAE)
Classification Metrics: AUC-ROC, F1 Score, Accuracy, Precision, Recall, False Positive/Negative Rates
Performance Benchmarking: Compared model results against published epigenetic clock studies
Research Methodology
Dataset Curation: Systematically identified and selected 11 studies meeting specific inclusion criteria from public repositories
Multi-Study Integration: Combined 4,303 samples across 9 studies for age prediction and 823 samples across 2 studies for disease classification
Experimental Design: Developed separate pipelines for age prediction (regression) and Alzheimer's classification (binary classification) tasks